Yesterday’s letter from HHS Secretary Sebelius was bland, but the attachment from CMS was more newsworthy.
First, no more extensions on the deadlines. The Exchanges will go live on January 1, 2014, as required in PPACA. If a state misses the deadline on Friday December 14, 2012 (this Friday), CMS will create a Federally-Facilitated Exchange. The state can apply later for subsequent years. HHS must approve or conditionally approve the State-Based Exchange by January 1, 2013, to be effective January 1, 2014. The only exception is for “State Partnership Exchanges,” for which the applications must be in by Feb. 15, 2013.
Second, the 100% federal match will not be available to states that use the Red State Option under the NFIB Supreme Court case. Partial expansions will not be subsidized (see Question 26 here).
Third, HHS hasn’t announced the methodology for DSH reductions (see Question 37 here). If HHS plays hardball here, following the statute, safety net hospitals in Red State Option states may suffer grave financial harm. To a significant degree, this harm will be self-inflicted by the states.
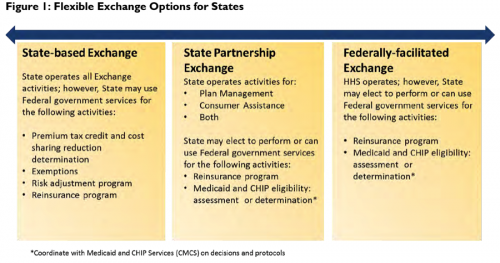
This seems like a good time to review the different types of Exchanges under the regulations:
- State-Based Exchange – created and run by a state, in conformity with PPACA, with the option to use some federal services.
- Federally-Facilitated Exchange — the back up exchange created by HHS when a state either fails to act or announces a decision not to create an exchange.
- State Partnership Exchange – a subset of Federally-Facilitated Exchange, where the state agrees to administer and operate some Exchange activities such as plan management and consumer assistance.
This handy chart is from CMS (the entire document is filled with useful details on the tasks that can be undertaken in the various types of Exchanges):
@koutterson